Abstract:
Primary Driving Pressure in Wood Vacuum Drying
Committee Chairman: Fred M. Lamb
The goal of these studies according to both theory and experimentation ended up being to prove the total pressure difference may be the primary driving pressure throughout the vacuum drying. The theoretical drying rates of diffusion, free water bulk flow and water vapor bulk flow were calculated and compared. The idea of equilibrium moisture content underneath the vacuum was created. The theoretical maximum moisture content stop by one cycle was calculated using energy balance. The model was created for that vacuum drying to know the mechanism from the vacuum drying such as the boiling front and it is movement.
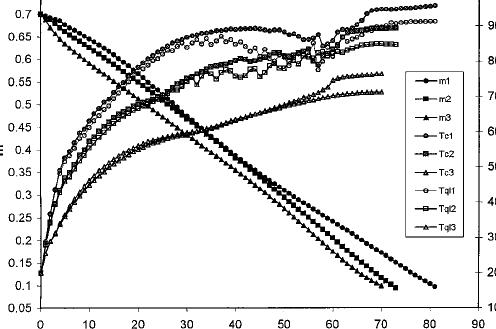
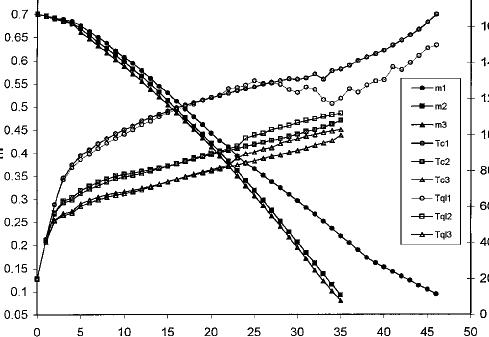
To judge the result from the sample size around the drying rate, four different thicknesses (1, 1.5, 2, 2.5 inches) and three different lengths (5, 10, 15 inches) were utilised. Within the cyclic drying, the examples were heated towards the 60 C. The vacuum was pulled to around 18 mm Hg. The vacuum pump was stored running for 140 minutes. It had been discovered that in cyclic vacuum drying, drying rate wasn’t impacted by the thickness. However, it had been impacted by the space. The cyclic drying curve was comprised of two distinct parts. The short drying period lasted about 10-20 minutes. The slow drying period happened next once the pressure inside wood got near to the ambient pressure.
In finish grain vacuum drying, the examples were coated with wax, covered with the plastic film and placed right into a rubber tube to avoid the moisture loss in the side surfaces during drying. The specimen size was 1ࡧ吆 inches. Red oak and white-colored oak were sealed and dried both in cyclic and continuous vacuum drying. The outcomes demonstrated that sealed examples dried almost as quickly as unsealed specimen.
There is little moisture loss in the side surfaces. There is a moisture gradient across the length both in cyclic drying and continuous vacuum drying.
Red oak examples of two.5ࡧ.5吆 inches were utilised to review the boiling front within the vacuum drying. To be able to identify the boiling phenomenon, the saturation pressures were calculated and were in contrast to the pressures simultaneously and same position. Boiling happened during drying and also the boiling front retreated to the middle of wood as drying began. The retreating speed relied on heat supply and also the permeability.
Vacuum drying at 70 degrees was investigated. The examples were dried at 20 C and pressure near 18 mm Hg. The outcomes demonstrated that wood could be vacuum dried at 70 degrees with little if any degrade in a reasonable drying rate.
All experimental results support the goal of this research the primary driving pressure may be the total pressure difference.
Listing of Attached Files
The writer grants to Virginia Tech or its agents the authority to archive and display their thesis or dissertation entirely or perhaps in part within the College Libraries of any type of media, now or hereafter known. The writer maintains all proprietary legal rights, for example patent legal rights. The writer also maintains the authority to use within future works (for example articles or books) any thing about this thesis or dissertation.
Abstract:
Primary Driving Pressure in Wood Vacuum Drying
Committee Chairman: Fred M. Lamb
The goal of these studies according to both theory and experimentation ended up being to prove the total pressure difference may be the primary driving pressure throughout the vacuum drying. The theoretical drying rates of diffusion, free water bulk flow and water vapor bulk flow were calculated and compared. The idea of equilibrium moisture content underneath the vacuum was created. The theoretical maximum moisture content stop by one cycle was calculated using energy balance. The model was created for that vacuum drying to know the mechanism from the vacuum drying such as the boiling front and it is movement.
To judge the result from the sample size around the drying rate, four different thicknesses (1, 1.5, 2, 2.5 inches) and three different lengths (5, 10, 15 inches) were utilised. Within the cyclic drying, the examples were heated towards the 60 C. The vacuum was pulled to around 18 mm Hg. The vacuum pump was stored running for 140 minutes. It had been discovered that in cyclic vacuum drying, drying rate wasn’t impacted by the thickness. However, it had been impacted by the space. The cyclic drying curve was comprised of two distinct parts. The short drying period lasted about 10-20 minutes. The slow drying period happened next once the pressure inside wood got near to the ambient pressure.
In finish grain vacuum drying, the examples were coated with wax, covered with the plastic film and placed right into a rubber tube to avoid the moisture loss in the side surfaces during drying. The specimen size was 1ࡧ吆 inches. Red oak and white-colored oak were sealed and dried both in cyclic and continuous vacuum drying. The outcomes demonstrated that sealed examples dried almost as quickly as unsealed specimen. There is little moisture loss in the side surfaces. There is a moisture gradient across the length both in cyclic drying and continuous vacuum drying.
Red oak examples of two.5ࡧ.5吆 inches were utilised to review the boiling front within the vacuum drying. To be able to identify the boiling phenomenon, the saturation pressures were calculated and were in contrast to the pressures simultaneously and same position. Boiling happened during drying and also the boiling front retreated to the middle of wood as drying began. The retreating speed relied on heat supply and also the permeability.
Vacuum drying at 70 degrees was investigated. The examples were dried at 20 C and pressure near 18 mm Hg. The outcomes demonstrated that wood could be vacuum dried at 70 degrees with little if any degrade in a reasonable drying rate.
All experimental results support the goal of this research the primary driving pressure may be the total pressure difference.
Listing of Attached Files
The writer grants to Virginia Tech or its agents the authority to archive and display their thesis or dissertation entirely or perhaps in part within the College Libraries of any type of media, now or hereafter known. The writer maintains all proprietary legal rights, for example patent legal rights. The writer also maintains the authority to use within future works (for example articles or books) any thing about this thesis or dissertation.




 Writing good research objectives for thesis
Writing good research objectives for thesis Torsten reil phd thesis writing
Torsten reil phd thesis writing Professor george saitoti thesis writing
Professor george saitoti thesis writing Device to device communication thesis proposals
Device to device communication thesis proposals Table of contents for psychology thesis proposal
Table of contents for psychology thesis proposal






