Consultant: Darrell J. Irvine and Patrick S. Doyle.
Department: Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Dept. of Chemical Engineering.
Author: Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Date Issued: 2008
Therapeutics for example proteins, DNA, or siRNA, could only exert their function within the cell cytosol or nucleus. However, many of them are cell membrane impermeable molecules that might just be adopted by cells via endocytosis or phagocytosis. Such drug molecules therefore are restricted in endolysosomes, where reduced pH and degradative enzymes may destroy them without therapeutic gain. Efficient escape of drug molecules for that cytosol before destruction in endolysosomes could be a major challenge for intracellular drug delivery. To deal with this problem, we produced a pH-sensitive core-covering nanoparticle to segregate the functions within the particle into an endosome-disrupting pH-responsive core that will absorb protons at endolysosomal pH, along with a covering whose composition might be tuned to facilitate particle targeting, cell binding, and drug binding. Two-stage surfactant-free emulsion polymerization of two-diethylamino ethyl methacrylate (DEAEMA) (core) and 2-amino ethyl methacrylate (AEMA) (covering) in the existence of a crosslinker was requested your synthesis of monodisperse core-covering hydrogel nanoparticles of 200 nm across. The protonation of tertiary amine groups across the polyDEAEMA core on moving from extracellular to endolysosomal pH introduced to reversible swelling within the nanoparticles obtaining a couple.8-fold diameter change.
Using pH-sensitivity of people nanoparticles, efficient cytosolic delivery of calcein (with
95% efficiency) was achieved by disrupting endolysosomes via proton sponge effect. The main amine wealthy covering was discovered to facilitate cell and drug binding, and provided minimal cytotoxicity by sequestering the proton sponge component within the direct interactions with cells. These particles proven a helpful approach to deliver therapeutic molecules for that cytosol of cells appealing efficiently.(cont.) The approval nanoparticles proven significant improvement in delivering one antigen vaccine protein ovalbumin (OVA) to primary dendritic cells for T cell activation, and promising knockdown of mRNA by delivering siRNA to epithelial cells for gene silencing. To enhance this method having a fully biodegradable system, nanoparticles obtaining a cleavable crosslinker bis (acryloyl) cystamine (BAC) were synthesized. Preliminary explorations in the approach proven that such particles can degrade in the existence of glutathione in vitro, a reducing peptide present at mM concentrations within the cytosol of mammalian cells. This design may be the drug releasing mechanism to boost delivery efficiency.
Thesis (Ph. D.)–Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Dept. of Chemical Engineering, 2008.This electronic version was printed using the student author. The certified thesis would be the Institute Archives and Special Collections.Vita.Includes bibliographical references (p. 193-208).
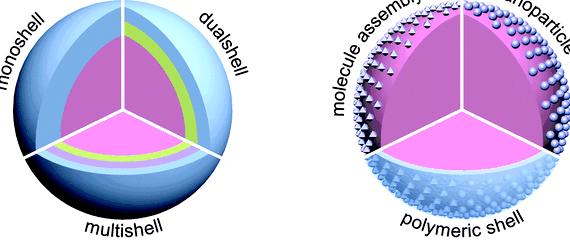
Keywords: Chemical Engineering.


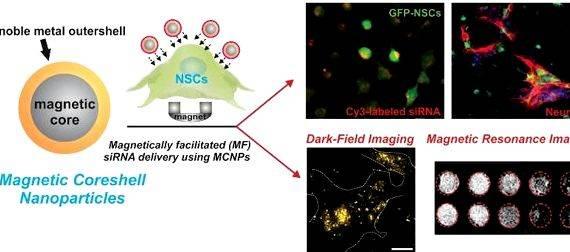


 Topic in english thesis proposal
Topic in english thesis proposal Locale of the study sample thesis proposal
Locale of the study sample thesis proposal Acknowledgement sample for architectural thesis proposal student
Acknowledgement sample for architectural thesis proposal student Face recognition attendance system thesis proposal
Face recognition attendance system thesis proposal Thesis proposal defense presentation ppt background
Thesis proposal defense presentation ppt background






