Photonic Very Fibre
Photonic very fibre (PCF) refers to a different group of optical fibre that is dependant on the options of photonic crystals. Because of its confinement characteristics or capacity of confining light in hollow cores, which isn’t achievable with usual optical fibre, photonic very fibre has been utilized in fibre lasers, communications involving fibre optics, high-power transmission, nonlinear devices, and highly sensitive gas sensors amongst others (Bjarklev, Bjarklev, Broeng, 2003). Specific kinds of photonic very fibre include hole fibre, photonic-bandgap fibre and Bragg fibre. Photonic-bandgap fibre describes PCFs, designed to use band gap effects to restrict light. Holey fibres make reference to PCFs that utilize air holes within their mix sections. They are also known as hole-aided fibres. Based on Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003), holey fibres are PCFs that guide light with a usual greater-index core that’s adapted to the existence of air holes. Bragg fibre is photonic-bandgap that’s created by circular multilayered film. PCFs are a subcategory of the general group of microstructured optical fibres, which utilizes not just a refractive index difference but additionally structural modifications to steer light (Jiang, 2008). In connection with this, this paper describes PCFs and discusses its construction and modes of operation.
Description of Phonic Very Fibres
Using the highly structured mix-portion of air spaces and glass, PCFs or microstructured fibres would be the ultimate niche fibre. Despite PCFs lately becoming commercially accessible, various kinds happen to be open to offer the fast growing selection of applications (Khan, 2008). Based on Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003), optical fibres appear to possess gone through evolution into many forms because the sensible breakthroughs that led to the broader introduction within the 1970 as always step index fibres and finally as solitary material fibres.
In solitary material fibres, propagation was achieved by efficient air cladding structure. Regular structured fibres, like photonic very fibres, have a normally uniform mix-section that’s microstructured from more a number of than a single material (Kili, 2008). Based on Kili (2008), the types of materials are often arranged periodically within the mix-portion of the fibre like a cladding that surrounds the main by which light is limited. For example, the very first shown photonic crystals made up of hexagonal pattern of air holes in silica fibre (Jiang, 2008). In 1996, the fibre were built with a solid core, although it was altered to some hollow core in 1998, in the center where light was limited. Other descriptions incorporated concentric rings made in excess of one material (Khan, 2008).
Bragg fibres and fibre Bragg gratings shouldn’t be confused. It is because they’re different (Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng, 2003). Fibre Bragg gratings include structural variation or intervallic refractive index across the axis from the fibre, instead of the improvement in the oblique directions, within the photonic very fibre. Both fibre gratings and PCFs make use of the phenomena of Bragg diffraction, although in different directions.
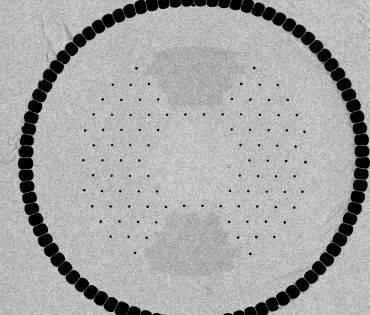
The cheapest recorded attenuation of solid core PCF is .37 dB/km (Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng, 2003).
Construction of Photonic Very Fibres
Photonic fibres are often built by similar techniques to individuals utilized in the making of other optical fibres. This process first includes setting up a preform on the proportions of centimetres in dimensions (Kili, 2008). The built preform will be heated and attracted lower to some smaller sized thickness. The thickness is often as smaller sized as those of real hair. However, the characteristics from the fibre continue to be maintained throughout the shrinking process (Jiang, 2008). As a result, countless kilometers could be manufactured from one preform. Typically the most popular approach to constructing photogenic fibre is stacking, though milling or drilling seemed to be accustomed to construct the earliest design. Based on Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003), this created the consequent grounds for constructing the very first polymer and soft glass structured fibres.
Jiang (2008) noticed that the majority of the photonic very fibres happen to be manufactured with silica. Nonetheless, other glasses are also found in acquiring certain optical qualities, such as the high optical non-linearity (Bjarklev, Bjarklev, Broeng, 2003). There appears to become an growing curiosity about the making of photonic very fibre from polymer (Kili, 2008). This interest has led to the wide search for various structures, for example ring structured fibres, graded index structures, and hollow core fibres. The 3 structures happen to be known as microstructured polymer optical fibres (MPOF) (Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng, 2003). A combination of chalcogenide glass and polymer has additionally been employed for wavelengths of 10.6 micrometer, especially in which the silica isn’t transparent (Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng, 2003).
Modes of Operation
Based on Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003), the modes of operation of photonic very fibre could be categorized into two distinct operational modes. Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003) noticed that these modes derive from the confinement mechanism utilized by the photonic very fibre. PCFs having a core getting a greater average index compared to microstructured covering operate while using index guiding principle, also is utilized in conventional optical fibre. Such PCFs that operate according to this principle can exhibit a greater effective refractive index backward and forward layers from the core and also the cladding (Jiang, 2008). Consequently, PCFs operating according to this principle can exhibit much robust confinement for applications in polarization-maintaining fibres and nonlinear optical devices.
The 2nd mode of operation could be in line with the development of photonic bandgap. Within this mode of operation, light is led by photonic bandgap that’s fabricated through the microstructured covering or cladding. Based on Khan (2008), this type of bandgap can confine light inside a hollow air core or perhaps a lower-index core if effectively designed. Khan (2008) reported that bandgap fibres getting hollow cores may possibly steer clear of the limits enforced through the present materials to create fibres, which confine light in wavelengths that materials aren’t available. Based on Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003), it is because the sunshine is majorly in mid-air, but away from the solid material. The hollow core has an additional advantage of enabling someone to introduce dynamically materials in to the core (Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng, 2003). Materials that may be introduced in to the hollow core include gases that should be tested for that accessibility to any substance (Bjarklev, Bjarklev, Broeng, 2003). Photonic very fibre may also be modified by since the holes with sol-gels of various or similar index material to be able to boost the light transmittance (Jiang, 2008).
Photonic very fibre (PCF) refers to a different group of optical fibre that is dependant on the options of photonic crystals. The 3 kinds of photonic very fibre include hole fibre, photonic-bandgap fibre and Bragg fibre. Despite PCFs lately becoming commercially accessible, various kinds happen to be open to offer the fast growing selection of applications. Regular structured fibres, like photonic very fibres, will often have a normally uniform mix-section that’s microstructured from more a number of than a single material. Photonic fibres are often generally built by similar techniques to individuals deployed within the output of other optical fibres. The majority of the photonic very fibres happen to be manufactured with silica. The modes of operation of photonic very fibre could be categorized into two distinct operational modes.
Photonic Very Fibre
Photonic very fibre (PCF) refers to a different group of optical fibre that is dependant on the options of photonic crystals. Because of its confinement characteristics or capacity of confining light in hollow cores, which isn’t achievable with usual optical fibre, photonic very fibre has been utilized in fibre lasers, communications involving fibre optics, high-power transmission, nonlinear devices, and highly sensitive gas sensors amongst others (Bjarklev, Bjarklev, Broeng, 2003). Specific kinds of photonic very fibre include hole fibre, photonic-bandgap fibre and Bragg fibre. Photonic-bandgap fibre describes PCFs, designed to use band gap effects to restrict light. Holey fibres make reference to PCFs that utilize air holes within their mix sections. They are also known as hole-aided fibres. Based on Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003), holey fibres are PCFs that guide light with a usual greater-index core that’s adapted to the existence of air holes. Bragg fibre is photonic-bandgap that’s created by circular multilayered film. PCFs are a subcategory of the general group of microstructured optical fibres, which utilizes not just a refractive index difference but additionally structural modifications to steer light (Jiang, 2008). In connection with this, this paper describes PCFs and discusses its construction and modes of operation.
Description of Phonic Very Fibres
Using the highly structured mix-portion of air spaces and glass, PCFs or microstructured fibres would be the ultimate niche fibre. Despite PCFs lately becoming commercially accessible, various kinds happen to be open to offer the fast growing selection of applications (Khan, 2008). Based on Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003), optical fibres appear to possess gone through evolution into many forms because the sensible breakthroughs that led to the broader introduction within the 1970 as always step index fibres and finally as solitary material fibres. In solitary material fibres, propagation was achieved by efficient air cladding structure. Regular structured fibres, like photonic very fibres, have a normally uniform mix-section that’s microstructured from more a number of than a single material (Kili, 2008). Based on Kili (2008), the types of materials are often arranged periodically within the mix-portion of the fibre like a cladding that surrounds the main by which light is limited. For example, the very first shown photonic crystals made up of hexagonal pattern of air holes in silica fibre (Jiang, 2008). In 1996, the fibre were built with a solid core, although it was altered to some hollow core in 1998, in the center where light was limited. Other descriptions incorporated concentric rings made in excess of one material (Khan, 2008).
Bragg fibres and fibre Bragg gratings shouldn’t be confused. It is because they’re different (Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng, 2003). Fibre Bragg gratings include structural variation or intervallic refractive index across the axis from the fibre, instead of the improvement in the oblique directions, within the photonic very fibre. Both fibre gratings and PCFs make use of the phenomena of Bragg diffraction, although in different directions. The cheapest recorded attenuation of solid core PCF is .37 dB/km (Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng, 2003).
Construction of Photonic Very Fibres
Photonic fibres are often built by similar techniques to individuals utilized in the making of other optical fibres. This process first includes setting up a preform on the proportions of centimetres in dimensions (Kili, 2008). The built preform will be heated and attracted lower to some smaller sized thickness. The thickness is often as smaller sized as those of real hair. However, the characteristics from the fibre continue to be maintained throughout the shrinking process (Jiang, 2008). As a result, countless kilometers could be manufactured from one preform. Typically the most popular approach to constructing photogenic fibre is stacking, though milling or drilling seemed to be accustomed to construct the earliest design. Based on Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003), this created the consequent grounds for constructing the very first polymer and soft glass structured fibres.
Jiang (2008) noticed that the majority of the photonic very fibres happen to be manufactured with silica. Nonetheless, other glasses are also found in acquiring certain optical qualities, such as the high optical non-linearity (Bjarklev, Bjarklev, Broeng, 2003). There appears to become an growing curiosity about the making of photonic very fibre from polymer (Kili, 2008). This interest has led to the wide search for various structures, for example ring structured fibres, graded index structures, and hollow core fibres. The 3 structures happen to be known as microstructured polymer optical fibres (MPOF) (Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng, 2003). A combination of chalcogenide glass and polymer has additionally been employed for wavelengths of 10.6 micrometer, especially in which the silica isn’t transparent (Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng, 2003).
Modes of Operation
Based on Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003), the modes of operation of photonic very fibre could be categorized into two distinct operational modes. Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003) noticed that these modes derive from the confinement mechanism utilized by the photonic very fibre. PCFs having a core getting a greater average index compared to microstructured covering operate while using index guiding principle, also is utilized in conventional optical fibre. Such PCFs that operate according to this principle can exhibit a greater effective refractive index backward and forward layers from the core and also the cladding (Jiang, 2008). Consequently, PCFs operating according to this principle can exhibit much robust confinement for applications in polarization-maintaining fibres and nonlinear optical devices.
The 2nd mode of operation could be in line with the development of photonic bandgap. Within this mode of operation, light is led by photonic bandgap that’s fabricated through the microstructured covering or cladding. Based on Khan (2008), this type of bandgap can confine light inside a hollow air core or perhaps a lower-index core if effectively designed. Khan (2008) reported that bandgap fibres getting hollow cores may possibly steer clear of the limits enforced through the present materials to create fibres, which confine light in wavelengths that materials aren’t available. Based on Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng (2003), it is because the sunshine is majorly in mid-air, but away from the solid material. The hollow core has an additional advantage of enabling someone to introduce dynamically materials in to the core (Bjarklev, Bjarklev Broeng, 2003). Materials that may be introduced in to the hollow core include gases that should be tested for that accessibility to any substance (Bjarklev, Bjarklev, Broeng, 2003). Photonic very fibre may also be modified by since the holes with sol-gels of various or similar index material to be able to boost the light transmittance (Jiang, 2008).
Photonic very fibre (PCF) refers to a different group of optical fibre that is dependant on the options of photonic crystals. The 3 kinds of photonic very fibre include hole fibre, photonic-bandgap fibre and Bragg fibre. Despite PCFs lately becoming commercially accessible, various kinds happen to be open to offer the fast growing selection of applications. Regular structured fibres, like photonic very fibres, will often have a normally uniform mix-section that’s microstructured from more a number of than a single material. Photonic fibres are often generally built by similar techniques to individuals deployed within the output of other optical fibres. The majority of the photonic very fibres happen to be manufactured with silica. The modes of operation of photonic very fibre could be categorized into two distinct operational modes.





 Monster theory 7 thesis writing
Monster theory 7 thesis writing Conceptual framework thesis definition in writing
Conceptual framework thesis definition in writing National institute of technology rourkela thesis writing
National institute of technology rourkela thesis writing Scope and limitations in thesis writing
Scope and limitations in thesis writing The revolution as a social movement thesis writing
The revolution as a social movement thesis writing






